The "Technocentric" View


ML Definition
Data
Data
"Information, especially facts or numbers, collected to be examined and considered and used to help decision-making, or information in an electronic form that can be stored and used by a computer." (Cambridge Dictionary, 2025)
Data Challenges
Data Challenges

Data Availability
Each ML project is unique and data can be scarce
- Specific requirements
- Domain
- Location
- Space
- ...
Data Challenges
Data Usability
ML Models require data in a specific format
- Structured vs Non-structured data
- Sparse data
- Legal regulations and privacy
- Storage technologies
- ...

Data Challenges
Data Quality Issues
ML Models are data-driven
- Missing values
- Duplicate records
- Incorrect data
- Outlier values
- ...

Data Challenges
Data Bias and Fairness
ML Models are data-driven
- Sampling bias
- Historical bias
- Measurement bias
- Algorithmic bias
- Implicit bias
- ...
Data Challenges
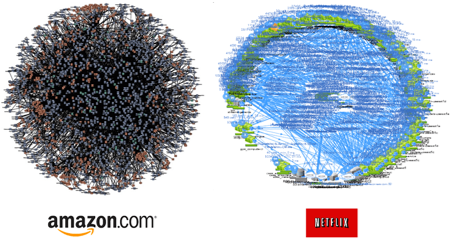
Data Complexity
Complex and dynamic systems
- Large systems
- Data generation speed
- Current systems architectures
- Interpretability issues
- Intellectual debt
- ...
Data-Orientation
Data-Orientation
Data-Orientation

Focus on Operations
Data-Orientation

Focus on Operations
Data-Orientation

Focus on Operations
- Separation of concerns
- High availability
- Scalability
- Low latency
Data-Orientation
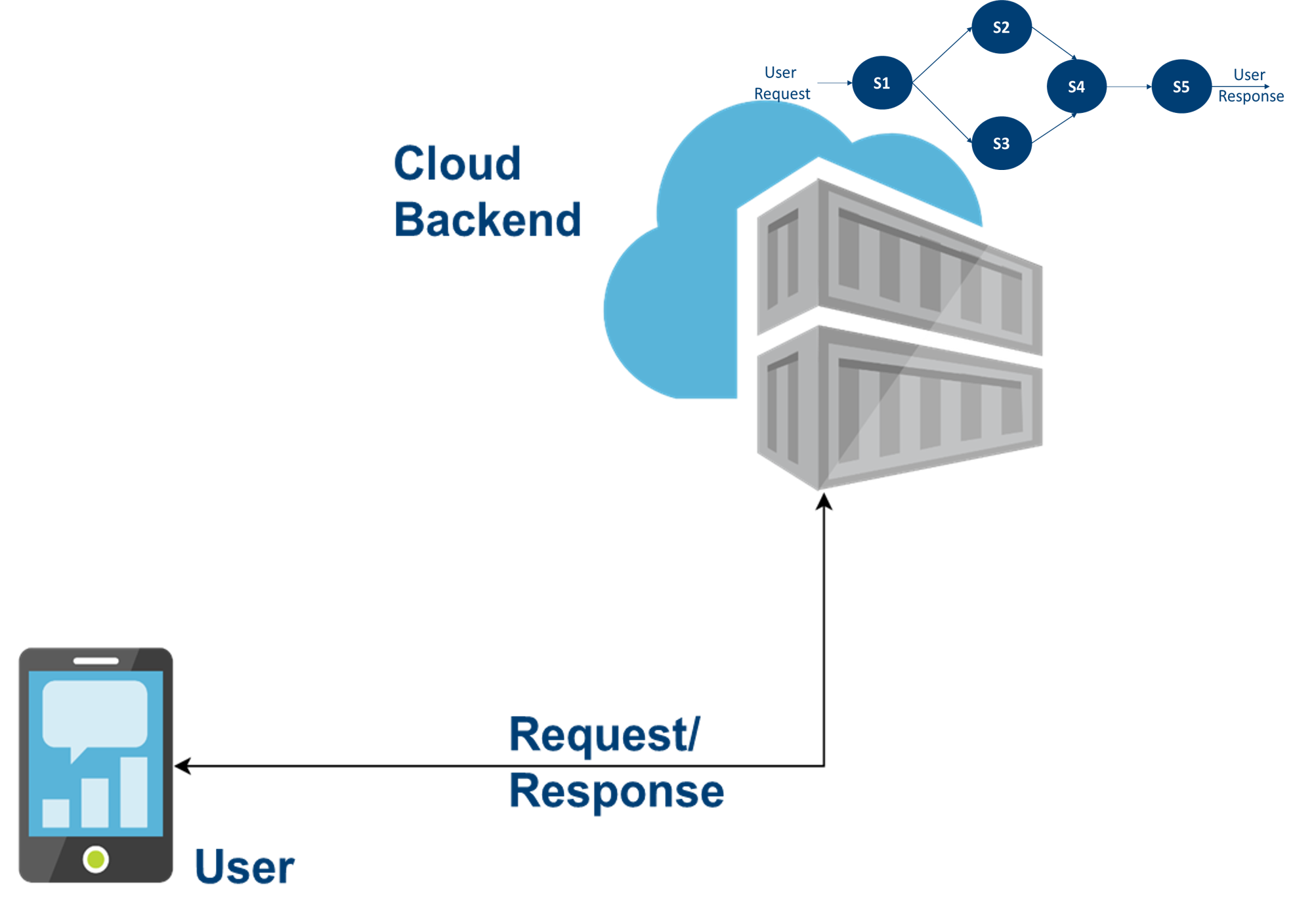
Focus on Operations
- Separation of concerns
- High availability
- Scalability
- Low latency
Data-Orientation

The Data Dichotomy
“While data-driven systems are about exposing data, service-oriented architectures are about hiding data.” (Stopford, 2016)
Data-Orientation
The Data Dichotomy
“While data-driven systems are about exposing data, service-oriented architectures are about hiding data.” (Stopford, 2016)
We need to design systems prioritising data!
Data-Orientation
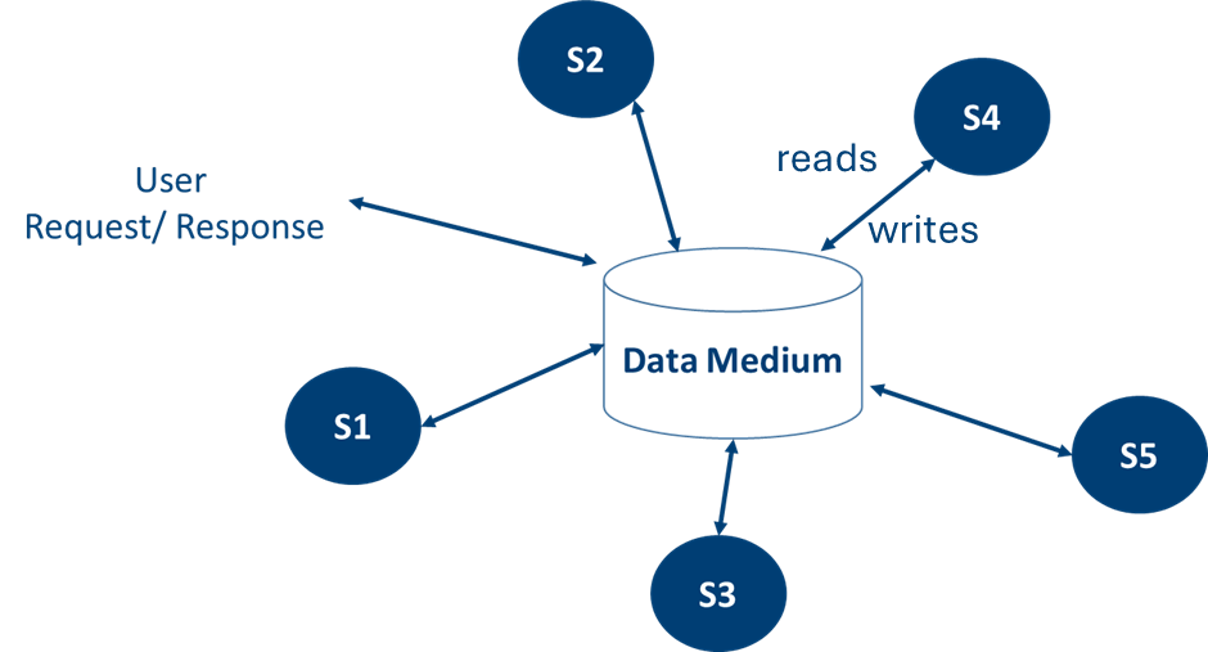
Data-Oriented Architectures
Data-First Systems
- Data is available by design
- Traceability and monitoring
- Interpretability
Data-Orientation

Data-Oriented Architectures
Data-First Systems
- Data is available by design
- Traceability and monitoring
- Interpretability
Data-Orientation
Data-Oriented Architectures
Prioritise Decentralisation
- Super-low latency requirements
- Privacy by design
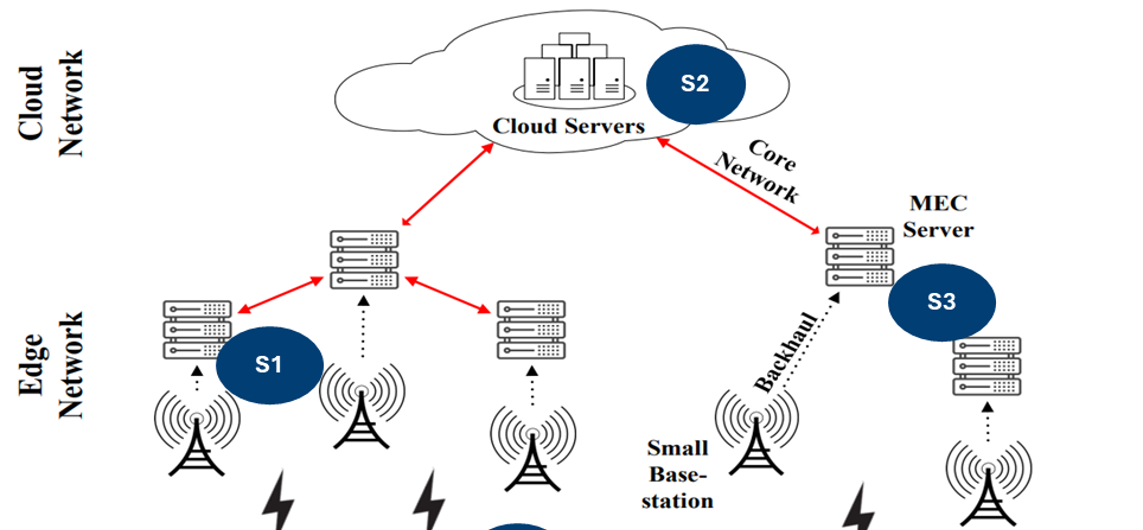
Data-Orientation
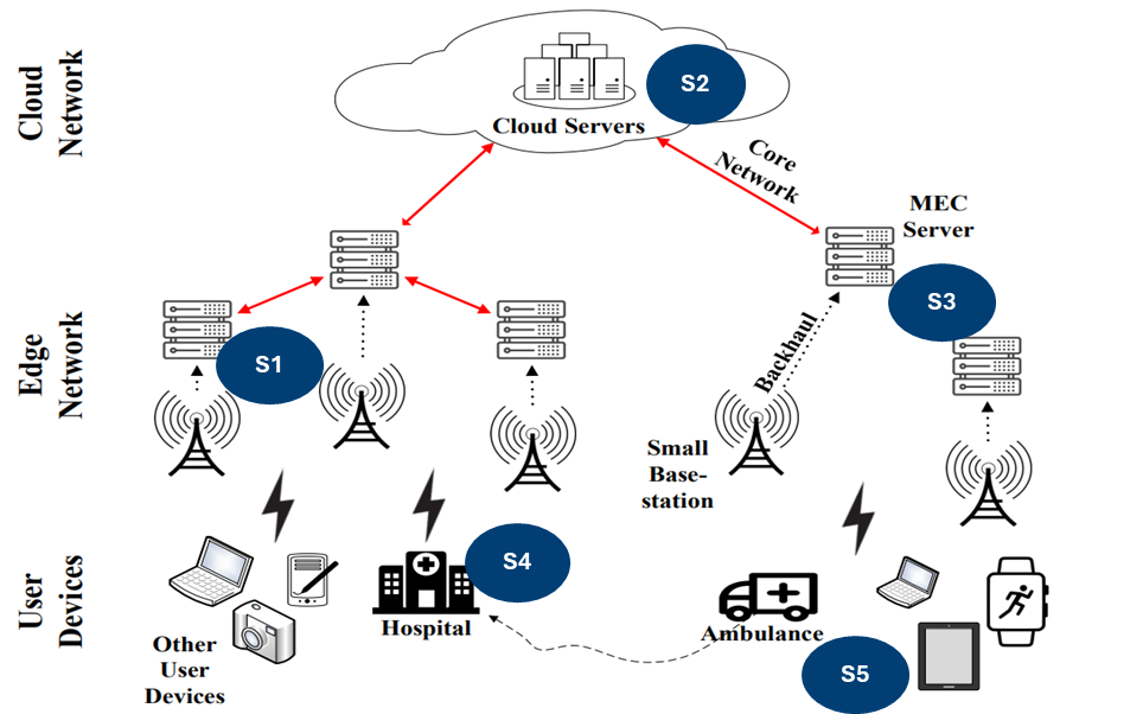
Data-Oriented Architectures
Openness
- Sustainable solutions
- Data ownership
Data-Orientation
The Data Science Process
The Data Science Process
The Data Science Process
The Data Science Process

The Data Science Process

Data Access
Data Access
Does the data even exist?
Data Access
No, it does not exist!
Data Access
Primary Data Collection
- Questionnaires
- Interviews
- Focus group interviews
- Surveys
- Case studies
- Process analysis
- Experimental method
- Statistical method
- ...
No, it does not exist!
Data Access
Primary Data Collection
- Questionnaires
- Interviews
- Focus group interviews
- Surveys
- Case studies
- Process analysis
- Experimental method
- Statistical method
- ...
- Expensive data collection processes
- Particular methodologies
- None fits all needs
Data Access
Yes, it does exist!
Data Access
Secondary Data Collection
- Published printed sources
- Books, journals, magazines, newspapers
- Government records
- Census data
- Public sector records
- Electronic sources (e.g., public datasets, websites, etc.)
- ...
Yes, it does exist!
Data Access
Secondary Data Collection
- Published printed sources
- Books, journals, magazines, newspapers
- Government records
- Census data
- Public sector records
- Electronic sources (e.g., public datasets, websites, etc.)
- ...
- Validity and reliability concerns
- Outdated data
- Relevancy issue
Data Access
Crash Map Kampala
- Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of death for the young in many contexts
- Data is difficult to access and made impossible any analysis of the problem
Data Access
Crash Map Kampala
- Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of death for the young in many contexts
- Data is difficult to access and made impossible any analysis of the problem
Data Access

Crash Map Kampala
- Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of death for the young in many contexts
- Data is difficult to access and made impossible any analysis of the problem
Data Access

Crash Map Kampala
- Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of death for the young in many contexts
- Data is difficult to access and made impossible any analysis of the problem
Data Access

Crash Map Kampala
- Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of death for the young in many contexts
- Data is difficult to access and made impossible any analysis of the problem
Data Access
The dataset creation is a critical process that cannot be skipped if we want to implement Data Science or ML projects
We can assume datasets exist, but they will likely enable toy projects not relevant for our society
Data Access
Data Access
Using your own files
The most common are comma separated values files (i.e., CSV files).
Data Access
Using your own files
The most common are comma separated values files (i.e., CSV files).
import pandas as pd
dataset = pd.read_csv('path/to/your/dataset.csv')
print("Dataset shape:", dataset.shape)
print("\nFirst few rows:")
print(dataset.head())
Data Access
Using built-in datasets
Different repositories are available online. For example, OpenML or Tensorflow datasets
Data Access
Using built-in datasets
Different datasets repositories are available online. For example, OpenML, an open source platform for sharing datasets and experiments.
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
iris = fetch_openml(name='iris', version=1, as_frame=True)
print("Iris dataset shape:", iris.data.shape)
print("\nFirst few rows:")
print(iris.data.head())
Data Access
Using built-in datasets
- The Iris dataset is a built-in dataset in scikit-learn
- It contains 150 samples of iris flowers, each with 4 features
- The target variable is the species of the iris flower
- It is commonly used for classification tasks
- Look at the dataset documentation, such as the Iris dataset documentation
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
iris = fetch_openml(name='iris', version=1, as_frame=True)
print("Iris dataset shape:", iris.data.shape)
print("\nFirst few rows:")
print(iris.data.head())
Data Access
Using built-in datasets
- Another popular dataset: CIFAR-10 from Tensorflow datasets
- Contains 60,000 32x32 color images
- 10 different classes
- Commonly used for image classification
import tensorflow as tf
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
print("Training data shape:", x_train.shape)
print("Test data shape:", x_test.shape)
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- APIs are interfaces that allow different systems to communicate with each other
- Servers expose these interfaces
- Clients consume these interfaces (i.e., client-server architecture)
- They communicate through the internet
import requests
url = '<url_of_the_dataset>'
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
with open("." + file_name_part_1, "wb") as file:
file.write(response.content)
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- The UK Price Paid data for housing in dates back to 1995 and contains millions of transactions
- This database is available at gov.uk
- The total data is over 4 gigabytes in size and it is available in a single file or in multiple files split by years and semester
- The example downloads the data for the first semester of 2020
import requests
url = 'http://prod.publicdata.landregistry.gov.uk.s3-website-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/pp-2020-part1.csv'
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
with open("." + file_name_part_1, "wb") as file:
file.write(response.content)
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- The UK Price Paid data for housing in dates back to 1995 and contains millions of transactions
- This database is available at gov.uk
- The total data is over 4 gigabytes in size and it is available in a single file or in multiple files split by years and semester
- The example downloads the data for the first semester of 2020
import requests
import pandas as pd
url = 'http://prod.publicdata.landregistry.gov.uk.s3-website-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/pp-2020-part1.csv'
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
with open("." + file_name_part_1, "wb") as file:
file.write(response.content)
dataset = pd.read_csv('pp-2020-part1.csv')
print("Dataset shape:", dataset.shape)
print("\nFirst few rows:")
print(dataset.head())
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- The OpenPostcode Geo dataset provides additional information about the houses
- It is a dataset of British postcodes with easting, northing, latitude, and longitude and with additional fields for geospace applications, including postcode area, postcode district, postcode sector, incode, and outcode
- This must be unzipped
import requests
import pandas as pd
import zipfile
import io
url = 'https://www.getthedata.com/downloads/open_postcode_geo.csv.zip'
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
with zipfile.ZipFile(io.BytesIO(response.content)) as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall('open_postcode_geo')
dataset = pd.read_csv('open_postcode_geo/open_postcode_geo.csv')
print("Dataset shape:", dataset.shape)
print("\nFirst few rows:")
print(dataset.head())
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- OpenStreetMaps (OSM) is a collaborative project to create a free editable map of the world. Explore OSM.
- OSM enables the creation of custom maps, geospatial analysis, and location-based services
- It is open source and anyone can access it
- The data lacks the structure we are used to
- We need to install the Python module first
%pip install osmnx
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- This example shows how to download the points of interest (POIs) of Pasto, Nariño, Colombia, using Python
import osmnx as ox
import pandas as pd
place = "Pasto, Nariño, Colombia"
pois = ox.features_from_place(place, tags={'amenity': True})
pois_df = pd.DataFrame(pois)
print(f"Number of POIs found: {len(pois_df)}")
print("\nSample of POIs:")
print(pois_df[['amenity', 'name']].head())
pois_df.to_csv('pasto_pois.csv', index=False)
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- We can also plot the city buildings
import osmnx as ox
import pandas as pd
place = "Pasto, Nariño, Colombia"
buildings = ox.features_from_place(place, tags={'building': True})
buildings.plot()
Data Access
Accessing data via APIs
- We can also plot the city buildings
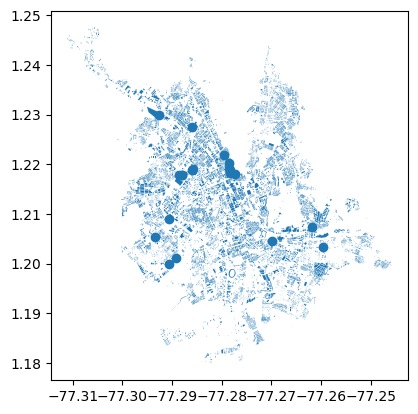
Data Access
Joining datasets
We can join multiple datasets to improve our data access
For example, the postcode dataset can enrich the UK Price Paid data by adding coordinates information. We should join these datasets using the common aspects between them (i.e., postcode).
Data Access
Joining datasets
We can join multiple datasets to improve our data access
For example, the postcode dataset can enrich the UK Price Paid data by adding coordinates information. We should join these datasets using the common aspects between them (i.e., postcode).
price_paid = pd.read_csv('pp-2020-part1.csv')
postcodes = pd.read_csv('open_postcode_geo/open_postcode_geo.csv')
merged_data = pd.merge(
price_paid,
postcodes,
on='postcode',
how='inner'
)
print("Original Price Paid dataset shape:", price_paid.shape)
print("Original Postcodes dataset shape:", postcodes.shape)
print("Merged dataset shape:", merged_data.shape)
print("\nSample of merged data:")
print(merged_data[['postcode', 'price', 'latitude', 'longitude']].head())
merged_data.to_csv('price_paid_with_coordinates.csv', index=False)
Data Access
Web scraping datasets
- Get the text from web pages
- Operate as a web explorer programmatically
- Parse the content, which can be unstructured
Data Access
Web scraping datasets
- Get the text from web pages
- Operate as a web explorer programmatically
- Parse the content, which can be unstructured
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
try:
url = '<url_of_the_website>'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
data = [p.text for p in soup.find_all('p')]
return data
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error scraping data: {str(e)}")
return None
Data Access
Creating synthetic datasets
- Mimics real-world variables and their relations
- Randomised generation of features
- Generation of target variables, representing feature relationships
- Relationships depend on expert's domain knowledge
Data Access
Creating synthetic datasets
- Mimics real-world variables and their relations
- Randomised generation of features
- Generation of target variables, representing feature relationships
- Relationships depend on expert's domain knowledge
import numpy as np
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, n_features)
y = np.zeros(n_samples)
for i in range(n_samples):
if X[i, 0] + X[i, 1] > 0:
y[i] = 0
elif X[i, 2] * X[i, 3] > 0:
y[i] = 1
else:
y[i] = 2
Conclusions
Conclusions
Overview
- Data definition and challenges
- Data-Orientation
- A Data Science Process
- Data Access
Conclusions
Overview
- Data definition and challenges
- Data-Orientation
- A Data Science Process
- Data Access
Next Time
- Data Quality
- Data Assess
- Data Address